Limitations of Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist
In certain situations, the front view camera or front radar sensor may not be able to detect the vehicle ahead. In these cases, Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist may not operate properly. The driver must pay careful attention in the following situations where Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist operation may be limited.
The sensor may be limited when:
-
Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist may not operate for 15 seconds after the vehicle is started or the camera is initialized.
-
Front view camera and front radar contaminated or blocked.
-
The camera lens is contaminated due to tinted, filmed or coated windshield, damaged glass, or stuck of foreign matter (sticker, bug, etc.) on the glass.
-
Inclement weather such as heavy rain or snow obscures the field of view of the radar sensor or camera.
-
There is interference by electromagnetic waves.
-
There is severe irregular reflection from the radar sensor.
-
The camera/radar sensor recognition is limited
-
The vehicle in front is too small to be detected. (for example a motorcycle etc.)
-
The vehicle in front is an oversize vehicle or trailer that is too big to be detected by the camera recognition function. (for example a tractor trailer, etc.)
-
The camera’s field of view is not well illuminated (either too dark or too much reflection or too much backlight that obscures the field of view).
-
The vehicle in front does not have their rear lights or their rear lights does not turned ON or their rear lights are located unusually.
-
The outside brightness changes suddenly, for example when entering or exiting a tunnel.
-
Light coming from a street light or an oncoming vehicle is reflected on a wet road surface such as a puddle in the road.
-
The field of view in front is obstructed by sun glare or head light of oncoming vehicle.
-
The windshield glass is fogged up; a clear view of the road is obstructed.
-
The vehicle in front is driving erratically.
-
The vehicle is on unpaved or uneven rough surfaces, or road with sudden gradient changes.
-
The vehicle is driven near areas containing metal substances as a construction zone, railroad, etc.
-
The vehicle drives inside a building, such as a basement parking lot.
-
The camera does not recognize the entire vehicle in front.
-
The camera is damaged.
-
The brightness outside is too low such as when the headlamps are not on at night or the vehicle is going through a tunnel.
-
The shadow is on the road by a median strip, trees, etc.
-
The vehicle drives through a tollgate.
-
The windshield glass is fogged up; a clear view of the road is obstructed.
-
The rear part of the vehicle in front is not normally visible. (the vehicle turns in other direction or the vehicle is overturned.)
-
The adverse road conditions cause excessive vehicle vibrations while driving.
-
The sensor recognition changes suddenly when passing over a speed bump.
-
The vehicle in front is moving vertically to the driving direction.
-
The vehicle in front is stopped vertically.
-
The vehicle in front is driving towards your vehicle or reversing.
-
You are on a roundabout and the vehicle in front circles.
-
Driving on a curved road
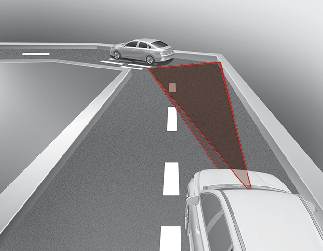
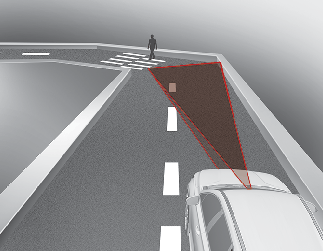
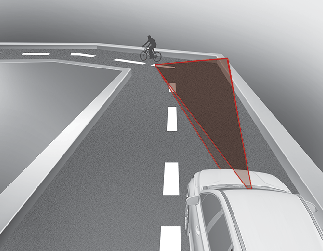
Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist may be limited when driving on a curved road.
The front view camera or radar sensor recognition system may not detect the vehicle, pedestrian or cyclist traveling in front on a curved road.
This may result in no alarm and braking when necessary.
Always pay attention to road and driving conditions, and if necessary, depress the brake pedal to reduce your driving speed in order to maintain a safe distance.
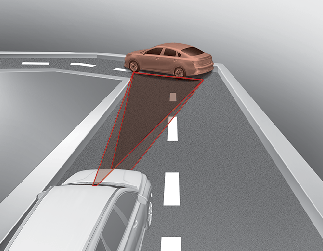
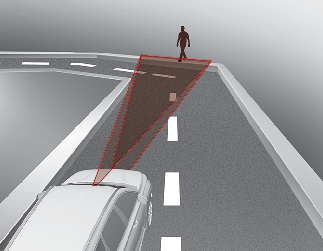
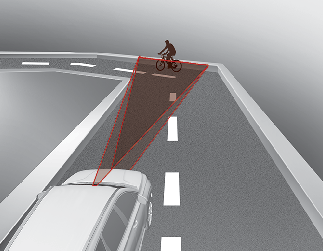
Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist may recognize a vehicle or pedestrian or cyclist in the next lane or outside the lane when driving on a curved road.
If this occurs, Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist may unnecessarily alarm the driver and apply the brake.
Always pay attention to road and driving conditions, while driving.
-
Driving on an inclined road


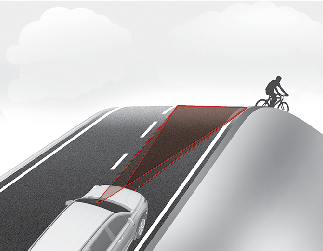
The performance of Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist may be decreased while driving upward or downward on a slope. The front view camera or front radar sensor recognition may not detect the vehicle, pedestrian or cyclist in front.
This may result in unnecessary alarm and braking or no alarm and braking when necessary.
When Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist suddenly recognizes the vehicle, pedestrian or cyclist in front while passing over a slope, you may experience sharp deceleration.
Always keep your eyes forward while driving upward or downward on a slope, and, if necessary, depress the brake pedal to reduce your driving speed in order to maintain distance.
-
Changing lanes
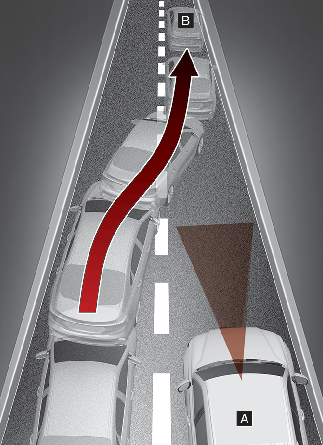
[A]: Your vehicle, [B]: Lane changing vehicle
When a vehicle changes lanes in front of you, Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist may not immediately detect the vehicle, especially if the vehicle changes lanes abruptly. In this case, you must maintain a safe braking distance, and if necessary, depress the brake pedal to reduce your driving speed in order to maintain a safe distance.
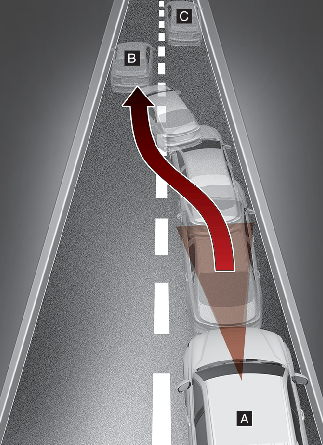
[A]: Your vehicle, [B]: Lane changing vehicle, [C]: Same lane vehicle
When driving in stop-and-go traffic, and a stopped vehicle in front of you merges out of the lane, Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist may not immediately detect the new vehicle that is now in front of you. In this case, you must maintain a safe braking distance, and if necessary, depress the brake pedal to reduce your driving speed in order to maintain a safe distance.
-
Detecting vehicle

When the vehicle in front has heavy loading extended rearward, or when the vehicle in front has higher ground clearance, it may induce a hazardous situation. Always pay attention to road and driving conditions, while driving and, if necessary, depress the brake pedal to reduce your driving speed in order to maintain distance.